ALL ABOUT ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTATION
Infrared Spectroscopy: Introduction and classification of Infrared radiation (IR)
By Amrita Shetty, 10 June 2021
Infrared spectroscopy is Spectroscopy study deal with the absorption of infrared radiation of electromagnetic spectrum by molecule. Mostly used by organic and inorganic chemist.
IR spectrum gives sufficient information about the
· Structure (identification of functional groups) of a compound.
· Assess the purity of a compound.
It is also known as vibrational-rotational spectroscopy is the absorption of infrared radiation by a molecule causes changes in their vibrational and rotational energy levels.
IR spectrum is divided into 3 main categories:
·· Far infrared (<400 cm−1)
· Mid-infrared (4000–400 −1)
· Near-infrared (13000–4000 cm−1)
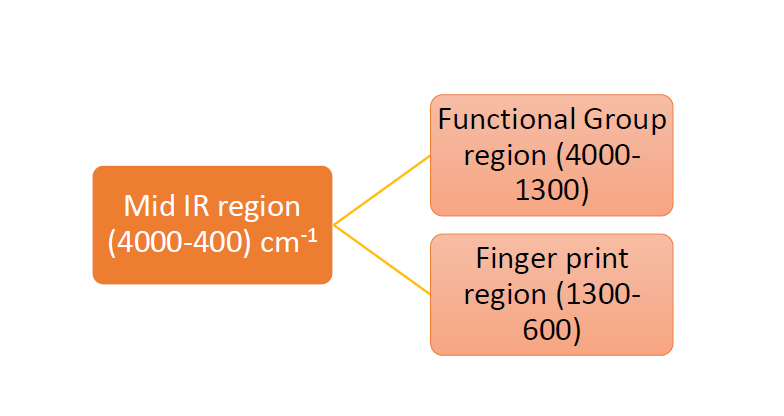
Mid IR spectrum is often used by chemist to identify organic molecule. Mid IR region are divided to two group.
Functional group region in which most of the functional groups present in organic molecules exhibits absorption bands in the region 4000-1300 cm-1. Finger print region is region from 1300 cm-1 to 600 cm-1 usually contains a very complicated series of absorptions are mainly due to molecular vibrations, usually bending motions that are characteristic of the entire molecule or large fragments of the molecule. The Functional group and Finger print region both are used because two molecules having the same functional group may show similar spectra in the functional group region but their spectra differ in the finger print region.
Near-infrared region (NIR) is weak intensity because absorptions observed in the near-infrared region (13000–4000 cm−1) are overtones or combinations of the fundamental stretching bands. In this region Hydrogen bonding, solute-solvent interactions, organometallic compounds, and inorganic compounds is analyzed.
Far- Infrared region is 600-100 cm-1. This region in which Organometallic and inorganic molecules contain heavy atoms and have weak bonds & lattice vibration of crystalline material occur in the FIR.

Comments
Post a Comment